Think of technical SEO issues as all the hidden, backstage problems that stop search engines from finding, understanding, and ranking your website. We're talking about everything from slow-loading pages and broken links to more complex errors that block Google's crawlers entirely. If these aren't fixed, even the most brilliant content can become practically invisible online.
Understanding Your Website's Technical Health
Let's use an analogy. Your website is like a high-performance car. The content—your blog posts, product pages, and stunning images—is the sleek paint job and premium leather interior. It's what everyone sees and loves. But what really matters for getting from point A to B is what's under the hood.
Technical SEO is your website's engine, transmission, and electrical system. It’s the behind-the-scenes machinery that determines how fast and reliably your site runs. If the engine is sputtering, it doesn’t matter how amazing the car looks; it’s not going to win any races. This guide is all about looking under that hood, without getting bogged down in confusing jargon.
The Core Purpose of Technical SEO
At its core, technical SEO is about one thing: making it incredibly easy for search engines like Google to do their job. Their automated bots, or "crawlers," need to be able to find, read, and make sense of every important page on your site without hitting any roadblocks. When they run into problems, they often just give up, leaving your best content undiscovered and unranked.
Most technical SEO issues boil down to three main problem areas:
- Crawlability and Indexability: Can search engine bots even get to your content and save it in their database? This is where you fix things like broken links, bad redirects, or a misconfigured robots.txt file that's accidentally blocking them.
- Performance and Speed: How fast does your site load for a real person? Page speed is a huge ranking factor, and a slow site will send visitors bouncing away before your content even appears.
- User Experience: Is your site secure? Does it work well on a phone? Can people find what they're looking for? Google wants to send its users to sites that are safe, mobile-friendly, and easy to navigate.
Ignoring these foundational elements is like driving with the check engine light on. Sure, you might make it down the road for a bit, but eventually, you’re going to find yourself broken down on the side of the digital highway, watching all your traffic and potential customers drive right by.
The best first step is a full-site review to see what's really going on. A detailed website audit checklist is a great way to guide that initial look. By keeping your site's technical health in check, you’re building a strong, reliable foundation that lets your great content finally get the attention it deserves.
Tackling Crawlability and Indexability Roadblocks
If a search engine bot can't get to your content, it might as well not exist. Think of Googlebot as a librarian trying to catalog every book in your website's massive library. If the doors are locked (a crawlability issue) or the books are in a language the librarian can't decipher (an indexability issue), they’ll never make it onto the public shelves.
Fixing these core technical SEO issues is all about handing search engines a VIP pass. You want them to explore every important corner, understand what each page is about, and add it to their enormous database—the index. If a page isn't in the index, it cannot rank. Period.
Making the Most of Your Crawl Budget
Google doesn’t have infinite time to spend on your site. It assigns a “crawl budget,” which is the amount of time and resources it will dedicate to exploring your pages. For bigger sites, this budget is gold. Wasting it on junk pages means your most important content might get ignored.
The goal is to gently guide crawlers toward your best pages and steer them away from the low-value stuff. This means cleaning up anything that sends them on a wild goose chase, like:
- Redirect Chains: Long strings of redirects (Page A to Page B to Page C) burn through your crawl budget before the bot even gets to the real content.
- Low-Value URLs: Think internal search results, endlessly filtered category pages, or old tag archives. These pages offer little unique value and should usually be blocked.
- Server Errors: If a crawler keeps hitting error pages, it might slow down its crawl rate, assuming your site is unstable.
By managing your crawl budget effectively, you're essentially telling Google, "Hey, focus your attention here on my best stuff." It's how you ensure your new blog posts and updated product pages get found fast.
Fixing Your Site's Rulebook and Roadmap
Two of the most important files for crawlers are your robots.txt file and your XML sitemap. The robots.txt file is like a bouncer at the door, telling bots which areas are off-limits. Your XML sitemap, on the other hand, is the friendly tour guide, handing them a map of all your important pages.
It's shockingly common for these files to be misconfigured, and the damage can be huge. Imagine launching a whole new e-commerce platform only to find out Googlebot can’t see it because of a setup error. This isn't just a hypothetical; research shows 23% of websites forget to link their sitemaps in robots.txt, and another 15% are missing a sitemap entirely. These are the kinds of mistakes that cause indexing nightmares and leave key pages collecting zero organic traffic.
Eliminating Common Indexing Blockers
Beyond those big-picture files, small on-page mistakes can stop a page from being indexed. A frequent culprit is a misplaced canonical tag. This tag is supposed to tell Google which version of a duplicate page is the "main" one. Point it to the wrong URL, and you've just told Google to ignore your important page in favor of another.
Similarly, "noindex" tags are powerful directives that tell search engines not to add a page to their index. They’re great for staging sites or private admin areas, but a stray noindex tag can make a critical landing page disappear from search results overnight.
If your website is not showing up in Google, a rogue noindex tag or a block in your robots.txt is often the first place to look. This is why regularly checking a tool like Google Search Console is non-negotiable—it helps you spot these roadblocks before they do real harm.
Boosting Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
In a world of short attention spans, a slow website isn't just a minor inconvenience—it’s a dead end for potential customers. Page speed has graduated from a nice-to-have feature to a cornerstone of user experience and a confirmed Google ranking factor. A sluggish site actively works against your efforts to attract and keep an audience.
Imagine this: you've launched a beautiful e-commerce store, but visitors leave in droves because pages take forever to load. This is the reality for the 72% of websites plagued by slow speeds, a critical technical SEO issue that torpedoes rankings. Google's Core Web Vitals directly penalize sites where content takes too long to appear, effectively pushing them down in search results.
Decoding Core Web Vitals
To speed things up, you first have to know what Google is looking for. Core Web Vitals are three specific metrics that measure the real-world experience a user has on your page. Think of them as a report card on how fast and usable your site feels.
-
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This tracks how long it takes for the main piece of content—like a hero image or a big block of text—to appear. It answers the user’s question: "Is this thing loading or not?" An LCP over 2.5 seconds is a problem.
-
Interaction to Next Paint (INP): This metric measures responsiveness. It clocks the time from when a user clicks a button or taps the screen to when the page visually responds. It answers: "Did my click actually do anything?"
-
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This one measures visual stability. It flags those frustrating moments when buttons or text jump around while the page is loading, causing you to click the wrong thing. It answers: "Is this page stable, or is it going to trick me?"
A poor Core Web Vitals score is a clear signal to Google that your site delivers a frustrating experience. Fixing these issues isn’t just about SEO; it’s about respecting your visitors’ time and making your site genuinely better.
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Speed Bumps
Finding the source of the slowdown is the first step. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights will give you a detailed breakdown, but the fixes usually fall into a few key areas. For a deeper technical understanding, exploring application performance optimization is a great next step.
Here’s a quick guide to some of the most common issues that drag down site speed and what you can do about them.
Common Site Speed Issues and How to Fix Them
| Issue | Description | Primary Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Oversized Images | Large, high-resolution image files take a long time to download, slowing down the initial page view. | Compress images to under 100 KB, use modern formats like WebP, and enable lazy loading for off-screen media. |
| Unoptimized Code | Bloated HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files with unnecessary characters (spaces, comments) increase load times. | Minify your code by removing extra characters and consider consolidating files to reduce server requests. |
| Slow Server Response | The web server itself is taking too long to respond to the initial request from a user's browser. | Upgrade your hosting plan, choose a host with better infrastructure, or implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN). |
| No Browser Caching | The site forces visitors to re-download all assets (logo, CSS) on every single visit. | Configure browser caching so that repeat visitors can load static files directly from their local device, making return visits much faster. |
These are just the starting points, but tackling them will make a huge difference in your site's performance.
A Closer Look at Fixes
Image and Media Optimization
Massive images are often the biggest and easiest speed problem to fix. When your site has to download huge, uncompressed files, it brings everything to a crawl and tanks your LCP score.
Actionable Fixes:
- Compress Images: Use tools to shrink file sizes without a major loss in quality. A good target is keeping most images under 100 KB.
- Use Next-Gen Formats: Switch from old-school JPEGs and PNGs to modern formats like WebP or AVIF, which offer superior compression.
- Implement Lazy Loading: This smart technique only loads images when a user is about to scroll them into view, dramatically speeding up the initial page load.
Code Minification and Caching
Messy or bloated code is another common performance killer. Minifying your CSS and JavaScript strips out all the unnecessary characters, making the files smaller and quicker to load.
On top of that, browser caching is a game-changer. It instructs a visitor's browser to save static files, like your logo and stylesheets. The next time they visit, the browser loads these saved files instantly instead of downloading them all over again. Our guide on how to optimize website performance provides a more detailed walkthrough.
By systematically finding and fixing these technical SEO issues, you can transform a slow, frustrating website into a fast, seamless experience that keeps users happy and drives conversions.
Strengthening Your Site's Security and Mobile Experience
Beyond pure speed and clean code, Google cares deeply about whether your site is a safe and accessible place for everyone, no matter what device they're using. Security and mobile-friendliness aren't just nice-to-haves anymore; they're core pillars of trust and usability that directly impact your rankings. Tackling these technical SEO issues is fundamental to building a website that both people and search engines can count on.
Think of it this way: site security is the digital equivalent of putting strong locks on your shop's doors. An old-school "HTTP" site is like leaving the front door wide open—it spooks visitors and signals to search engines that you don't take their safety seriously.
HTTPS Is Non-Negotiable
Flipping the switch to HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) across your entire site is one of the most important security upgrades you can make. It encrypts the connection between a visitor's browser and your website, shielding sensitive data like login details or payment information from prying eyes.
Google started using HTTPS as a ranking signal all the way back in 2014. Today, it’s just the cost of entry. Browsers like Chrome will plaster a "Not Secure" warning on any site still using HTTP, which is a surefire way to kill visitor trust and send your bounce rate through the roof.
Getting your site fully secured with an SSL certificate isn't just a box-ticking exercise. It's a clear signal to your visitors that you value their privacy and security. That trust is the foundation of a great user experience.
Watch out for "mixed content" errors, which happen when some parts of your site load over secure HTTPS but others (like images or scripts) still load over insecure HTTP. These errors can break parts of your page and trigger those scary security warnings, completely undermining all your hard work. The only right way to do it is to go all-in on HTTPS, everywhere on your site.
Winning in a Mobile-First World
The majority of all web traffic now happens on a phone, so it’s no surprise that Google has fully embraced mobile-first indexing. This simply means that Google predominantly uses the mobile version of your site to index and rank its pages. If your website is a clunky mess on a phone, your rankings will take a hit everywhere—even for people searching on a desktop.
A truly mobile-friendly site is more than just a shrunken-down version of your desktop design. It's about rethinking the experience for someone on the move.
Common Mobile Usability Headaches to Fix:
- Content Wider Than Screen: Nothing is more annoying than having to scroll side-to-side just to read a line of text. This is an instant user experience killer.
- Clickable Elements Too Close Together: When buttons and links are jammed on top of each other, fat-fingering the wrong link is inevitable for touchscreen users.
- Text Too Small to Read: If visitors have to pinch-to-zoom to read your content, your site isn't mobile-friendly. It’s that simple.
- Viewport Not Set: This is a bit of code that tells browsers how to properly scale your page to fit the device's screen. Forgetting it often leaves mobile users looking at a tiny, shrunken version of your desktop site.
Fixing these issues is about more than just keeping Google happy. It’s about making your site genuinely usable for the huge chunk of your audience on their phones. A modern, responsive design that automatically adapts to any screen size is the standard today. By smoothing out these user experience bumps, you're creating a better journey for every visitor, and that's exactly what search engines are designed to reward.
Clarifying Your Content with Structured Data
Getting search engines to see your website is only half the battle. To really make an impact, you need them to understand it. That's where structured data (often called Schema markup) comes in.
Think of it as a translator. You’re taking the content that makes perfect sense to a human visitor and adding a special layer of code that speaks directly to search engine bots. It’s like giving Google a cheat sheet for your page.
This isn't just about keywords. It's about context. Without structured data, a search engine might see the numbers "4.8" and "$29.99" on a page and not know what they mean. With it, you're explicitly telling Google, "This is a product with a 4.8-star rating, and its price is $29.99." That small clarification changes everything.
Turning Data Into Rich Snippets
The real payoff for using structured data shows up right on the search results page. When Google gets this extra context, it can upgrade your standard blue link into a much more compelling rich snippet.
These enhanced listings pull in helpful details that catch the user's eye and answer their questions before they even click.
- E-commerce Product: Imagine showing star ratings, review counts, price, and availability right in the search results.
- Local Business: Your listing could feature opening hours, your address, and a click-to-call phone number.
- Recipe Blog: You can display the cooking time, calorie count, and a mouth-watering photo of the dish.
- FAQ Page: Google can show your questions and answers in a handy dropdown format directly under your main link.
Rich snippets aren't just for looks. They offer instant value, which makes searchers far more likely to click on your result instead of a competitor's plain one. Skipping structured data is a huge missed opportunity and a common technical SEO blind spot.
Implementing Schema on Your Site
Adding code to your site might sound like a job for a developer, but getting started with Schema is easier than you think. Most modern content management systems and SEO plugins have built-in tools that handle the basics for you, no coding required.
By properly implementing structured data, you are no longer just a listing in the search results; you're providing a direct, informative answer. This is a fundamental shift in how your site communicates its value to both users and search engines.
If you need to create something more custom, you don't have to write it from scratch. Online tools can do the heavy lifting. A handy Schema Markup Generator can build the right code for you. Just plug in your page details, and it will generate the markup for you to add to your site’s HTML. It’s a simple fix for a critical technical issue.
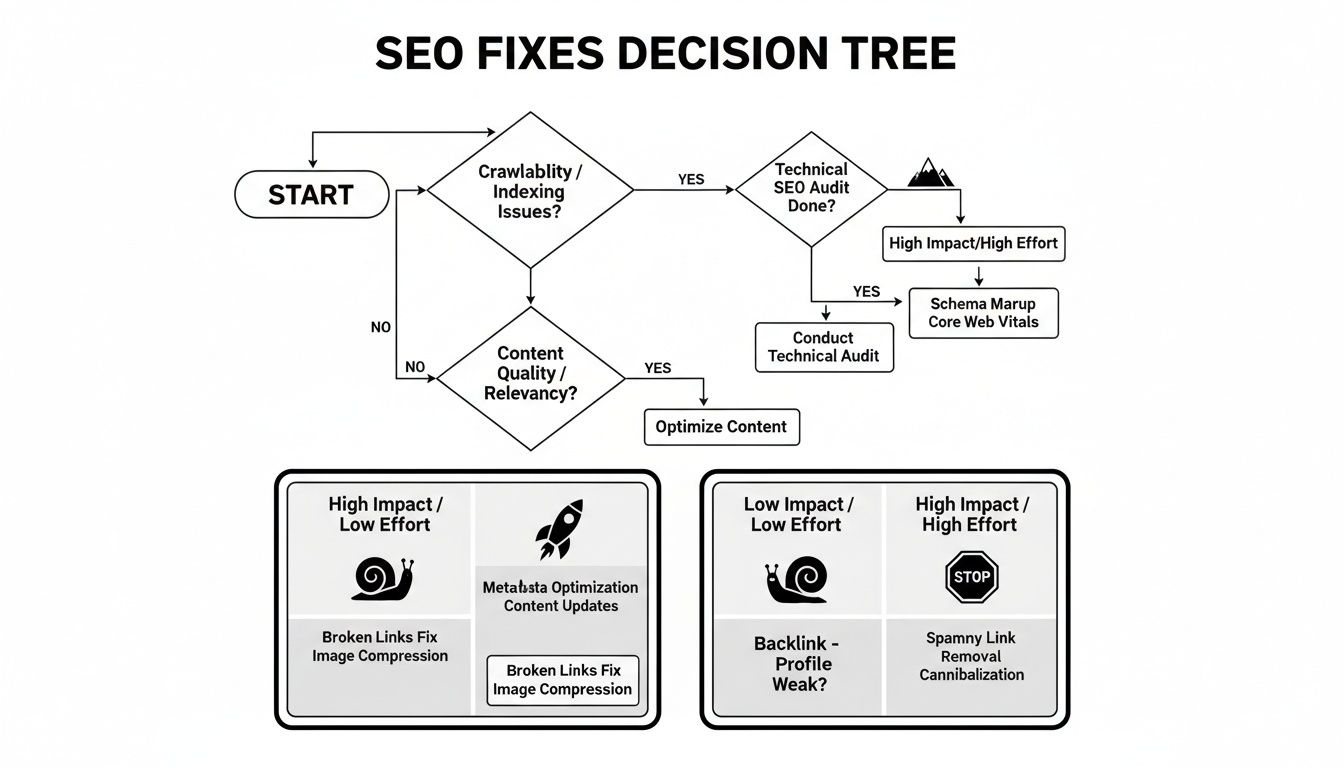
How to Diagnose and Prioritize Your SEO Fixes
Finding a long list of technical SEO issues can feel like opening the hood of your car and seeing a dozen warning lights blinking at once. It’s overwhelming. The secret isn't to start fixing every little thing, but to think like a seasoned mechanic: figure out what's most critical and tackle it in the right order. This is how you spend your time and budget on the things that will actually make a difference.
Your first stop should always be a couple of essential (and free) tools. Google Search Console is basically your direct line to Google. It’ll tell you straight up about major problems with indexing, mobile usability, and security. Spend time in the "Pages" report—it’s a goldmine for seeing which URLs are indexed correctly and which ones are hitting a wall.
Next up, run your site through Google PageSpeed Insights. This tool breaks down your site's performance for both mobile and desktop users. You’ll get a detailed report card on your Core Web Vitals and, more importantly, a list of specific, actionable advice like "reduce unused JavaScript" or "properly size images." It hands you a ready-made to-do list for speed improvements.
How to Decide What to Fix First
Okay, you've got your list of problems. Now comes the hard part: what do you fix today, and what can wait? A simple framework can help you cut through the noise. Just think about each issue based on two things: its potential impact on your SEO and user experience, and the effort it will take to fix it.
This approach helps you sort every task into a clear priority list.
Here’s a simple way to think about it, using a prioritization matrix. This isn't about complex spreadsheets; it's about making smart, quick decisions.
Technical SEO Issue Prioritization Matrix
| Priority Level | Issue Examples | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| P1: Quick Wins | Fixing a robots.txt file that blocks your whole site, removing a rogue noindex tag, submitting a correct XML sitemap. |
Fix Immediately. These are high-impact, low-effort tasks. They offer the biggest bang for your buck and can produce noticeable results quickly. |
| P2: Major Projects | A full site migration to HTTPS, overhauling site architecture, implementing a comprehensive structured data plan. | Plan and Schedule. These are high-impact, high-effort projects. They are critical for long-term success but require careful planning, resources, and a dedicated timeline. |
| P3: Fill-in Tasks | Adding missing alt text to a few old images, cleaning up a handful of broken internal links, optimizing a few meta descriptions. | Do When Time Allows. These are low-impact, low-effort fixes. They're good to chip away at between larger projects but won't sink your site if they wait a bit. |
| P4: Back Burner | Spending days overhauling your entire URL structure for a minor keyword benefit, micro-optimizing code that has no real user impact. | Re-evaluate or Ignore. These are low-impact, high-effort tasks. The return on investment is often too low to justify the work. Keep them on a "maybe later" list. |
This "website triage" approach lets you make smart, strategic decisions instead of just reacting.
Think of it this way: a site-wide indexing error is a five-alarm fire. It needs your full attention right now. A few pages with slightly long meta descriptions? That's more like a slow, dripping faucet. You'll get to it, but it's not an emergency.
Knowing the difference is what separates panicked, wheel-spinning activity from focused, strategic progress. By concentrating on the high-impact fixes first, you ensure that every hour you spend on technical SEO issues is an hour that genuinely moves the needle.
Common Questions About Technical SEO
Diving into technical SEO can feel a bit overwhelming, and it's natural to have questions about how long things take, who you need on your team, and where to even start. I hear these same questions all the time from business owners trying to get a handle on their site's health. Let's clear up some of the most common ones.
How Often Should I Run a Technical SEO Audit?
Think of a technical audit less like a one-off project and more like a regular health check for your website. You wouldn't wait years between doctor's visits, right? Same principle applies here.
For most businesses, running a full audit every 3-4 months is a great rhythm. It’s frequent enough to catch problems before they spiral out of control but not so often that it becomes a burden.
That said, some events demand an immediate deep dive. You should always run an audit:
- After a website redesign or migration: This is a huge one. Things almost always break during major overhauls, from links to redirects.
- Following a major Google algorithm update: When Google changes the rules of the game, you need to see how your site stacks up.
- If you see a sudden, unexplained drop in traffic: A technical glitch is often the silent killer behind a sharp performance nosedive.
Do I Need a Developer to Fix Most SEO Issues?
This is a classic "it depends" situation, but I can give you a clearer breakdown. The good news is that you can fix many common technical SEO issues yourself without ever touching a line of code.
Things like updating meta titles and descriptions, fixing broken internal links, or adding alt text to your images are typically manageable right inside your CMS, whether it's WordPress or Shopify. Many SEO plugins even let you generate a new XML sitemap with a single click.
But for the heavier lifting, you'll definitely want a developer. Call in the experts for tasks like:
- Minifying CSS and JavaScript to improve site speed.
- Implementing complex custom Schema markup.
- Fixing slow server response times.
- Making fundamental changes to your website’s architecture.
This decision tree gives a great visual for how to think about prioritizing fixes based on how much impact they'll have versus the effort required.
My advice? Always start with the high-impact, low-effort fixes. These are your quick wins—the changes that can deliver real results without a massive development project.
How Long Does It Take to See Results After a Fix?
Here’s where you need to be patient. SEO is a long game, and the results from technical fixes don’t happen overnight. The time it takes to see a change really boils down to two things: the severity of the problem and how often Google crawls your site.
For a major, show-stopping issue—like accidentally blocking your entire site in the robots.txt file—you could see things bounce back within a few days to a week once Google notices the change. But for more subtle improvements, like boosting your page speed, it might take several weeks or even a couple of months for Google to recrawl those pages, process the improvements, and adjust your rankings accordingly.
The key is to keep an eye on your Google Search Console account. Once you see that Google has recrawled your updated pages, you know the process has started.
At Sugar Pixels, we specialize in taking the complexity out of technical SEO, allowing you to focus on your business while we handle the fixes. Build and scale your online presence with us today!