Slow-loading pages aren't just a minor inconvenience; they're a direct hit to your revenue, user trust, and even your search engine rankings. A delay of just a few seconds is often all it takes for a potential customer to click away, directly impacting your bottom line and how people see your brand.
The Business Cost of a Slow Website
It's easy to think of a slow website as a technical problem for the IT department to sort out. That's a huge mistake. Sluggish pages are a critical business issue with very real financial consequences. Every millisecond of delay adds friction to the customer's experience, chipping away at their trust and sending them straight to your competitors.
Think of it this way: the longer a visitor has to wait, the less likely they are to ever become a customer. For an e-commerce store, a two-second delay at checkout can send cart abandonment rates through the roof. For a startup trying to generate leads, a slow landing page means fewer sign-ups and a much higher cost to acquire each one. It doesn't matter what your business model is—speed is tied directly to revenue.
How Speed Shapes User Perception
Beyond the immediate loss of a sale, poor performance does lasting damage to your brand's reputation. A fast, snappy website feels professional and reliable. A slow one just feels broken and untrustworthy. That first impression is incredibly hard to overcome. Users who have a bad experience are far less likely to come back or recommend you to others.
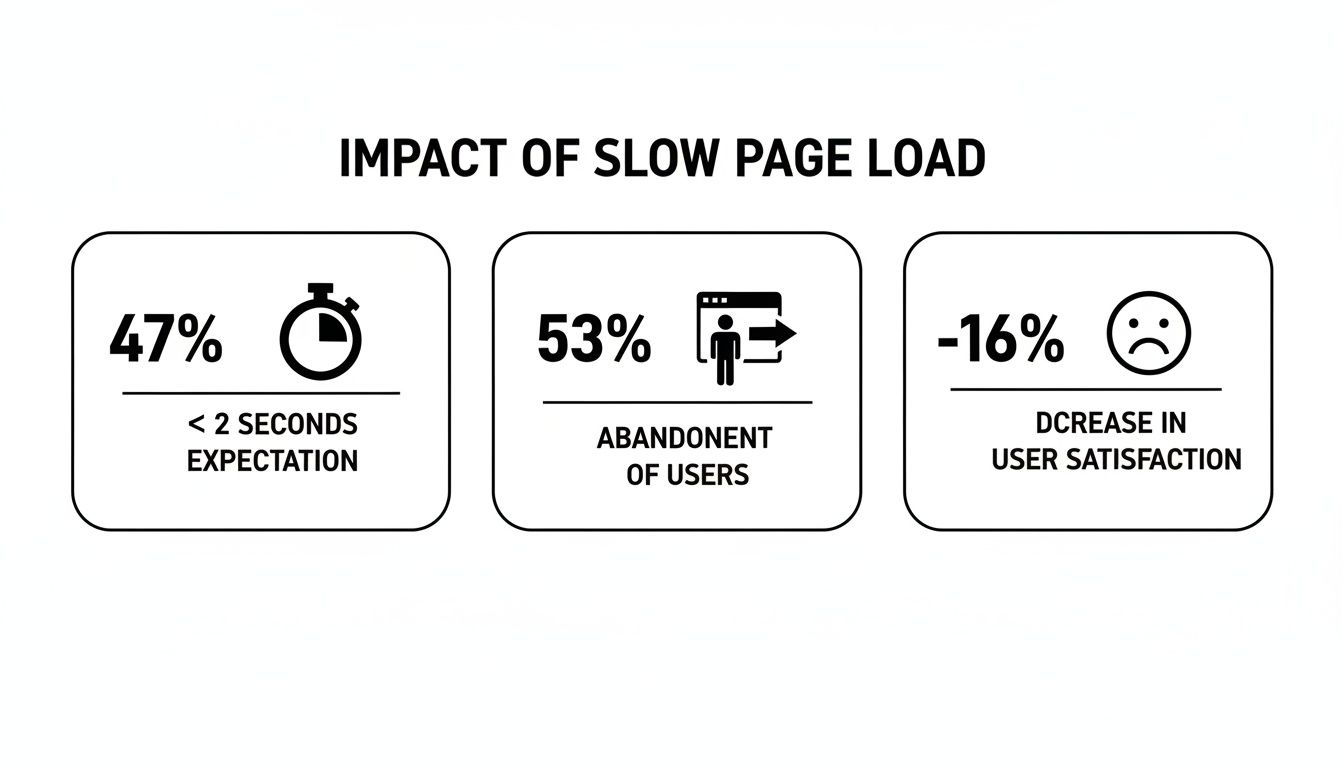
The data on user expectations is pretty unforgiving.
As you can see, the window to grab someone's attention is tiny, and the penalty for missing it is severe.
The Undeniable Data on Page Speed
The link between website speed and business results isn't just a theory; it's backed by a mountain of data. Consider these numbers: 47% of users expect a page to load in two seconds or less. A whopping 53% will abandon a site if it takes more than three seconds to load on a mobile device.
The financial impact is just as clear. Each one-second delay can slash user satisfaction by 16%. You can learn more about these website speed findings and see how they're affecting businesses today.
The table below breaks down just how much every second of delay can cost your business.
The Business Impact of Every Second Lost
| Load Time Increase | Impact on Conversions | Impact on Bounce Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 to 3 seconds | Conversion rate drops by 32% | Bounce rate increases by 32% |
| 1 to 5 seconds | Conversion rate drops by 40% | Bounce rate increases by 90% |
| 1 to 6 seconds | Conversion rate drops by 45% | Bounce rate increases by 106% |
| 1 to 10 seconds | Conversion rate drops by 50%+ | Bounce rate increases by 123% |
These figures show a direct and painful correlation: as load time goes up, your key metrics go down.
The core takeaway is simple: a slow website actively works against your business goals. It drives away customers, harms your brand, and ultimately reduces your profitability.
It's time to start treating page speed as a core business KPI. When you invest in performance, you're not just making a technical upgrade. You're making one of the smartest investments you can in user experience, customer retention, and your long-term success.
You can't fix a problem you don't understand. Before you start tweaking code or compressing images, you need a clear, unbiased picture of how your website is actually performing for your visitors.
Simply loading your site on your own computer doesn't count. Your browser has files cached, and your internet connection is likely miles faster than what your average user is working with. To really diagnose slow loading pages, you need objective data from the right tools.
These tools do more than just spit out a single "speed score." They break down the entire loading process, moment by moment, showing you exactly where the bottlenecks are. This is the difference between blindly guessing what's wrong and knowing precisely what to fix first.
Picking the Right Tools for the Job
There are a handful of excellent, free tools out there for testing site speed, and each gives you a slightly different angle. My advice? Use a couple of them to get a well-rounded view. The three I trust most are Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest.
For this guide, we're going to lean heavily on Google PageSpeed Insights. Why? Because its metrics directly mirror what Google itself uses for ranking signals—the all-important Core Web Vitals. Nailing these is a win for both your SEO and your users.
Here’s what they measure:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How long does it take for the main event—the largest image or block of text—to show up? You want this to be under 2.5 seconds.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): When a user clicks a button or taps a menu, how quickly does the page react? A good score here is under 200 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How much do things jump around on the screen while the page is loading? This is incredibly annoying for users, and you need to keep it below 0.1.
Getting familiar with these three metrics is your first real step. They tell a story about how a real person perceives your site's performance, which is infinitely more valuable than a simple "page load time."
It's easy to get fixated on the big "Performance" score at the top of the report. Don't. The real gold is buried in the "Opportunities" and "Diagnostics" sections—that's where the tool gives you a specific, actionable to-do list.
How to Read a Performance Report
Running a test is the easy part. Knowing what to do with the mountain of data it throws back at you is where the skill comes in.
When you plug a URL into PageSpeed Insights, you’ll get a report that shows two types of data: what it found in a controlled "lab" test and what real users are experiencing in the "field." It also breaks down scores for mobile and desktop, which are often wildly different.
The red and orange numbers are your roadmap. They point directly to the user experience problems you need to solve. If you're looking to conduct a more thorough analysis, our website audit checklist provides a structured way to look at performance alongside other critical site health factors.
Lab Data vs. Field Data: What's the Difference?
This is a concept that trips a lot of people up, but it's crucial.
Lab Data: This is a performance snapshot taken in a controlled setting. The tool uses a specific device and a throttled network connection to simulate a typical user. It’s perfect for debugging because the conditions are always the same, letting you see if your changes actually worked.
Field Data: This is the real deal. Also called Real User Monitoring (RUM), this data is collected anonymously from actual Chrome users who have visited your site over the last 28 days. It shows you how your site performs in the messy real world—on different devices, slower networks, and from various locations.
Field data is your ground truth.
If your lab tests look great but your field data is poor, you have a problem. It means that while your site performs well under ideal conditions, it's failing your actual users.
For instance, your lab test might report a zippy LCP of 2.1 seconds. But then you see your field data shows an LCP of 4.3 seconds. This is a huge clue! It tells you that a significant number of your visitors, likely those on slower mobile connections, are having a sluggish experience. That insight is pure gold—it tells you to stop worrying about desktop and focus your efforts on optimizing for mobile.
Your Action Plan for Common Speed Bottlenecks
Okay, you’ve run the tests and have the data. Now for the fun part: making things faster. When it comes to slow pages, a few usual suspects are almost always to blame. Forget chasing tiny, insignificant tweaks. We're going after the big wins that your visitors will actually feel.
Let's dive into the most practical, high-impact fixes, starting with the heaviest thing on almost every website: the images.
Tame Your Images (Before They Slow You Down)
I can't tell you how many times I've seen a beautiful site brought to its knees by gigantic, unoptimized images. A single high-resolution photo can easily be larger than all of your site's code, fonts, and scripts combined. Thankfully, this is one of the easiest and most rewarding problems to fix.
The game plan is simple: shrink image file sizes without ruining the quality, and use modern, efficient formats.
- Compress Everything: Never upload an image straight from your camera or designer. First, run it through a compression tool. I use TinyPNG all the time, but services like ImageOptim are also fantastic. You can often cut file sizes by 50-70% with virtually no visible difference. Many CMS platforms also have plugins that do this automatically.
- Switch to Modern Formats: It’s time to move beyond JPG and PNG. Convert your images to a next-gen format like WebP, which offers far better compression. A WebP image often looks just as good (or better) than a JPG but at a fraction of the file size. This single change can massively reduce the total data a visitor needs to download.
Once your images are lean, the next step is to control when they load. That's where lazy loading comes in. It's a clever trick that tells the browser, "Don't bother loading images that are off-screen until the user actually scrolls down to them."
Implementing this is surprisingly easy. Just add loading="lazy" to your image tags.
 This is now built into all modern browsers, making it one of the simplest performance boosts you can get.
This is now built into all modern browsers, making it one of the simplest performance boosts you can get.
Minify Your Code and Scripts
Every comment, space, and line break in your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files helps developers stay organized, but to a browser, it's just dead weight. Getting rid of all that unnecessary baggage is a process called minification.
Think of it like this: you're stripping down a race car by removing every non-essential part. Your code files become smaller, lighter, and much quicker for the browser to download and process.
Most website platforms and build tools can handle this for you. If you're on WordPress, for example, popular plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Rocket have a simple checkbox to enable minification for your CSS and JavaScript. Don't skip this—it's a foundational step for a speedy site.
The cumulative effect of these small optimizations is significant. Shaving even a few kilobytes off a dozen different files can add up to a full second of saved load time, especially on mobile connections where every byte counts.
Put Browser Caching to Work for You
Browser caching is a powerful way to make your site feel lightning-fast for repeat visitors. It works by telling a visitor's browser to save certain files—like your logo, stylesheets, and scripts—on their local device.
The next time they visit, their browser doesn't have to re-download everything from your server. Instead, it just pulls the files from its local cache. The result? Near-instant page loads.
You can set this up by adding a few rules to your server's .htaccess file. This little snippet tells browsers to hang onto different file types for specific amounts of time.
Re-Evaluate Your Hosting Foundation
I've seen it countless times: a team optimizes everything perfectly, but the site is still slow. In these cases, the problem isn't the website—it's the ground it's built on. If your Time to First Byte (TTFB) is high no matter what you do, your hosting is almost certainly the bottleneck.
Cheap shared hosting plans force your site to compete for resources with hundreds of others on the same server, which is a recipe for slow, inconsistent performance.
The data doesn't lie. The top 100 websites load in an average of 2.5 seconds on desktop, but that number skyrockets to 8.6 seconds on mobile. With 68% of traffic now coming from mobile devices, that's a massive problem. For e-commerce sites, the stakes are even higher: a site that loads in 1 second sees 2.5 times higher conversion rates than one that takes 5 seconds.
If you've hit a wall, it may be time to upgrade from shared hosting to a VPS or a quality managed host that guarantees resources. A solid server is the foundation of a fast website. If you're not sure where to start, our guide on how to choose a web host breaks down the options.
For a deeper dive into all the metrics that matter, this Core Web Vitals & Page Experience Playbook is an excellent resource. Getting these fundamentals right creates a faster, more reliable foundation for your entire online presence.
Taking Performance to the Next Level
So, you’ve done the basics. You've compressed your images, minified your code, and sorted out your browser caching. That's a huge step, but to get a site from just "fast" to "blazing fast," you need to think bigger. We're talking about how your content travels across the internet and how your server handles the pressure. This is where the pros separate themselves.
Think about a global e-commerce brand gearing up for a massive holiday sale. They've optimized every line of code, but they have customers from Sydney to Seattle. The sheer physical distance between a shopper in Australia and their server in Virginia creates an unavoidable delay. This delay, known as latency, is precisely what a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is designed to crush.
Get Closer to Your Users with a Content Delivery Network
A CDN is essentially a web of servers strategically placed around the globe. It takes copies of your site's static files—images, CSS, JavaScript—and stores them in these locations. When someone visits your site, the CDN serves those files from the server that's physically closest to them, slashing latency and making load times feel almost instant.
Instead of every single visitor from around the world hammering your one origin server, the traffic gets spread out. That e-commerce customer in Sydney? They'll download product images from a server right there in a Sydney data center, not from one on the other side of the planet.
Services like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront are leaders in this space. Cloudflare, in particular, has a fantastic free plan that’s more than enough for many businesses to get started. Often, setting it up is as simple as changing your domain's DNS settings to point to the CDN.
A CDN isn't just about speed. It's a huge security upgrade, too. It can help fend off DDoS attacks and often includes bonus features like automatic image optimization and code minification right at the network edge, taking even more work off your server.
Master the Critical Rendering Path
The critical rendering path sounds technical, but the concept is simple: it's the series of steps a browser has to take to turn your code into a visible webpage. Optimizing this path is all about getting the most important, "above-the-fold" content to appear as quickly as humanly possible, even if other parts of the page are still loading.
It's about making a great first impression. Here’s how you do it:
- Inline Critical CSS: Figure out the bare minimum CSS needed to style what a user sees without scrolling. Then, stick that code directly inside the
<head>of your HTML. This lets the browser start painting the page right away, without waiting for an external CSS file to download. - Defer Non-Critical CSS: Load the rest of your stylesheets asynchronously. This tells the browser, "Don't wait for this file to render the page; grab it when you have a free moment."
- Move Your JavaScript: Shove any non-essential JavaScript, especially those pesky third-party tracking scripts, to the very bottom of your HTML, just before the closing
</body>tag. Use thedeferorasyncattributes on your script tags to stop them from blocking the rest of the page from loading.
With this approach, your user sees a functional page in a flash, which drastically improves their perception of your site's speed. We go into much more detail on these techniques in our guide on how to optimize website performance.
Give Your Database a Tune-Up
If you're running on a platform like WordPress, a sluggish database is a classic, and often overlooked, cause of slow loading pages. Every time a page loads, WordPress has to make dozens of calls to the database to fetch content, user info, and plugin settings. If those queries are slow, everything grinds to a halt.
Regular maintenance is non-negotiable. This means cleaning out old post revisions, trashing spam comments, and getting rid of data left behind by uninstalled plugins. A plugin like WP-Optimize can automate a lot of this for you.
For high-traffic sites, it's worth looking into an object cache like Redis or Memcached. These tools store the results of common database queries in your server's super-fast memory. This means fewer trips to the database, resulting in a massive performance gain.
When to Upgrade Your Performance Stack
Knowing when to stick with DIY fixes versus calling in the pros (or investing in professional-grade tools) is key. If you're hitting a wall with the basics, it might be time to level up your hosting, CDN, or even consider a code refactor. This table can help you decide.
| Performance Issue | DIY Solution (Starter) | Professional Service (Growth/Scale) |
|---|---|---|
| Slow global load times (high latency) | Basic free CDN plan (e.g., Cloudflare free tier). | Premium CDN with more PoPs, advanced caching, and image optimization. |
| Site crashes during traffic spikes | Optimize code, enable page caching via plugins. | Upgrade from shared hosting to a dedicated server or managed cloud hosting. |
| Slow backend/admin area (e.g., WordPress) | Regular database cleanup with a plugin (e.g., WP-Optimize). | Implement an object cache (Redis/Memcached), hire a dev for query tuning. |
| Complex codebase is becoming unmanageable | Follow best practices for new features, minify existing code. | Hire an agency or freelancer for a partial or full code refactor. |
Ultimately, investing in your performance stack isn't just an expense; it's an investment in user experience and scalability. When your site is your business, ensuring it's fast and reliable is one of the smartest moves you can make.
Validating and Monitoring Your Speed Improvements
Making changes to fix slow loading pages without measuring the outcome is a bit like shooting arrows in the dark. You might hit something, but you'll never really know which arrow worked or if you missed the target completely. A methodical approach to validation and monitoring is what separates a few amateur tweaks from professional-grade performance optimization.
This isn't just about getting a pat on the back for a job well done. It's about protecting your live website. The absolute last thing you want is for a well-intentioned "fix" to crash your checkout process right in the middle of a flash sale. This is why you should never, ever work directly on your live site.
The Staging Environment: Your Safety Net
A staging environment is your best friend in this process. Think of it as an exact, private clone of your website where you can test your optimizations without any risk to your actual users. Before you even think about pushing that new caching rule or minified script to the world, you deploy it to staging first.
Here, you can run the same performance tools you used for diagnosis, like PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix, to get a clean "before and after" picture. Did your LCP score actually improve? Did you accidentally make the Cumulative Layout Shift worse? A staging site gives you the hard data to answer these questions with confidence.
This simple, disciplined step ensures that by the time a change goes live, you already know it's both safe and effective. It turns a risky guessing game into a reliable, repeatable process.
Using A/B Testing to Prove ROI
Let's be honest, not all speed improvements are created equal. Optimizing your images is a no-brainer. But what about a more complex change, like refactoring your critical CSS? The impact might not be so obvious. This is exactly where A/B testing shines.
A/B testing, also known as split testing, lets you show two different versions of your site to different groups of visitors at the same time.
- Version A (The Control): Your current, unchanged website.
- Version B (The Variant): The version with your shiny new performance optimization applied.
By running an A/B test, you can measure if the faster version actually leads to better business results. Does Version B have a higher conversion rate? A lower bounce rate? This is how you connect technical work directly to the bottom line. For instance, you might discover that enabling a CDN (Version B) increases your e-commerce conversion rate by a statistically significant 3% over two weeks. That’s powerful data you can take straight to your boss or stakeholders.
Proving that a $50/month investment in a premium CDN directly led to an extra $2,000 in monthly sales is how you justify performance budgets. A/B testing gives you the hard evidence to show the real return on investment of your optimization efforts.
Setting Up Proactive Performance Monitoring
Fixing your site's speed is a fantastic achievement, but performance isn't a one-and-done project. It’s an ongoing commitment. New plugins, updated content, and pesky third-party scripts can all introduce new bottlenecks, causing your site to slowly get sluggish again.
This is why setting up automated, continuous monitoring is non-negotiable. Tools like GTmetrix or Pingdom can be set up to test your key pages on a regular schedule—daily, or even every hour. You can establish performance budgets and set thresholds for your most important metrics.
For example, you could configure an alert to ping you on Slack or via email if your homepage's LCP ever creeps above 3 seconds. This proactive approach means you’ll often find out about a performance problem long before your customers do. You can pinpoint the exact day a regression happened, which makes it infinitely easier to identify the cause—like that new marketing plugin someone installed—and fix it quickly.
This whole system of checks and balances—staging, testing, and monitoring—creates a virtuous cycle. It makes sure your site not only gets fast but stays fast, protecting both the user experience and your revenue.
Your Website Speed Questions, Answered
Even with the best plan, you're bound to have questions. It's totally normal. Getting a handle on the common myths and sticking points around site performance is what gives you the confidence to push forward and get real results. Let's tackle some of the questions I hear all the time when it comes to fixing slow-loading pages.
Think of this as the final piece of the puzzle. We'll clear up any lingering confusion and make sure you're ready to make a genuine impact.
How Long Should a Page Take to Load?
While there's no single magic number, the data points to a clear target. For the best user experience and a solid SEO foundation, aim for a Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) of under 2.5 seconds. That’s the official "good" threshold from Google's Core Web Vitals.
But context is key here. If you're running an e-commerce site, the bar is even higher. Study after study shows conversion rates take a nosedive after just three seconds of load time. So, while under 2.5 seconds is a fantastic goal, for any site where transactions happen, every millisecond counts.
Will a CDN Really Help My Small Business Website?
Yes, absolutely. This is one of the biggest myths out there. So many small business owners think a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is an enterprise-only tool for massive global companies, but that just isn't true anymore. Even if your entire audience is local, a CDN delivers a serious performance boost.
Here's how a CDN can speed things up for you:
- Takes the Load Off: By serving images, scripts, and other assets from its own optimized network, a CDN frees up your server to focus on what it does best—generating the actual page content.
- Handles Optimizations for You: Many modern CDNs can automatically compress images or convert them to next-gen formats like WebP, saving you a ton of manual work.
- Adds a Layer of Security: They can act as a shield, helping to fend off common threats like DDoS attacks long before they ever get a chance to hit your server.
With providers like Cloudflare offering incredibly powerful free plans, a CDN has become a no-brainer for businesses of all sizes.
You can't make your website "too fast" from a user's perspective. However, there is a point of diminishing returns where the cost and effort of shaving off a few extra milliseconds might not provide a noticeable ROI. Focus on the major wins first.
Can My Website Be Too Fast?
From a user’s perspective? Not a chance. No visitor has ever complained that a page loaded too quickly. But from a business and resource standpoint, you can definitely hit a point of diminishing returns.
Once you’ve tackled the big wins—optimizing your images, setting up solid caching, getting on a decent hosting plan, and implementing a CDN—the effort it takes to shave off each additional millisecond skyrockets. The goal should be a tangibly fast and smooth experience for your users, not chasing a perfect 100/100 score on a performance tool just for the sake of it. Always prioritize the fixes that give you the biggest bang for your buck first.
At Sugar Pixels, we turn slow, frustrating websites into fast, high-converting digital experiences. If you're tired of watching potential customers bounce because of slow pages, our team can pinpoint the bottlenecks and implement performance fixes that drive real business growth. Let's build a faster website together.