If you want to speed up your website, a few core tasks will give you the biggest wins right away: optimizing your images, minifying your code, and using browser caching. These aren't just technical chores; they're the bedrock of a fast, smooth user experience that keeps people coming back.
Why A Fast Website Is No Longer Optional
Before we get into the nuts and bolts, let’s talk about what’s really at stake here. A slow website isn't just a minor inconvenience anymore—it’s a direct hit to your traffic, your leads, and your sales. We live in an age of impatience, and every single millisecond you can shave off your load time makes a real difference to your bottom line.
Slow performance is a triple threat: it drives visitors away, hurts your search engine rankings, and kills your conversion rates. That's why making your site faster isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a must-do.
This score isn't just a vanity metric. It’s a snapshot of your site's health that tells you exactly how users and search engines see you.
The High Cost of a Slow-Loading Page
The numbers don't lie—a slow website actively costs you money. Consider that 40% of online shoppers will leave a site that takes more than three seconds to load. That's almost half your potential customers gone before they even see your products.
As load times creep up, bounce rates skyrocket. A page that loads in five seconds has a 38% higher bounce rate than one that loads faster. People just don't stick around. Even their engagement plummets; a site loading in two seconds gets an average of 8.9 page views, but that drops to just 3.3 pages if the load time hits eight seconds.
This data paints a very clear picture: speed is a fundamental part of a great user experience. When you build a faster site, you'll see benefits almost immediately.
- Better User Engagement: When your site is responsive, visitors are happy to click around, read more content, and see what you have to offer.
- More Conversions: A snappy, quick-loading site removes frustration from the user journey, which means more sales, more sign-ups, and more leads.
- Improved SEO: Google has been very clear that page speed is a ranking factor. Faster sites get rewarded with better visibility in search results.
"A one-second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions. For an e-commerce site making $100,000 per day, a 1-second page delay could potentially cost you $2.5 million in lost sales every year."
In the end, every bit of effort you invest in your site's performance pays for itself. Even if you're a beginner just learning how to build a website, making speed a priority from the very start will set you up for success down the road.
Finding and Fixing Your Performance Bottlenecks
Before you even think about compressing a single image or minifying a line of code, you have to know what you’re up against. You can’t fix what you can’t find. This is the detective phase, where we use some fantastic tools to uncover exactly what’s putting the brakes on your website's speed.
My first stop is always a combination of Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix. It’s easy to get fixated on that big letter grade at the top, but the real gold is buried in the details. These reports are your treasure map, showing you which files are bloated, which scripts are holding up the show, and how long your server is taking to even start the conversation.
Decoding the Core Web Vitals
To make sense of these reports, you need to speak the language, and that language is Core Web Vitals. These aren't just arbitrary numbers; Google designed them to measure what a real person actually experiences when they land on your page.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This is all about perceived load speed. It measures the time it takes for the main event—the largest image or block of text—to appear on the screen.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): A newer metric, this one gauges responsiveness. How quickly does your site react when someone clicks a button or taps a link? A low INP means your site feels quick and alive.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This one tracks visual stability. You know when you try to click something, and an ad loads, pushing the button down the page? That’s a high CLS, and it’s incredibly frustrating for users.
For the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), you're aiming for a time under 2.5 seconds. Anything more, and you're testing people's patience. And let's be honest, they don't have much. Nearly half of all visitors expect a page to load in two seconds or less, and a staggering 40% will bounce if it takes longer than three.
Think of a low score in PageSpeed Insights not as a failure, but as a personalized roadmap. It points out exactly where you should direct your efforts for the most significant impact, whether that’s shrinking images or tackling render-blocking code.
From Diagnosis to Action Plan
Once you’ve run a test, ignore the score for a moment and scroll straight down to the "Opportunities" and "Diagnostics" sections. This is your checklist. PageSpeed Insights doesn't just tell you something is wrong; it gives you a list of the specific culprits.
You might see a suggestion like "Properly size images," complete with a list of the exact image files that are way bigger than they need to be. Or it might flag "render-blocking resources," pointing to the specific CSS and JavaScript files that are preventing your page from loading until they're fully downloaded.
Nailing this diagnostic step is the key to improving website loading speed. It takes the whole process from a frustrating guessing game to a clear, prioritized to-do list.
If all the technical jargon feels a bit much, this report is the perfect document to give a professional. When you choose a web design agency, handing them this data gives them a crystal-clear starting point. For a much deeper dive into the technical side of things, this guide on Application Performance Optimization is an excellent resource. By focusing on these specific bottlenecks, every single change you make will deliver a real, measurable improvement.
Winning the Battle Against Heavy Assets
Once you’ve pinpointed the performance bottlenecks, it’s time to deal with the most common things slowing your site down: heavy assets. I'm talking about those massive images and bloated code files that act like anchors on your load times. Getting your page weight down is one of the single most effective things you can do to speed things up.
The connection between page size and load time is painfully direct. In fact, a large webpage can take a staggering 318% longer to visually load than a smaller one. The good news? There's a lot of low-hanging fruit here. Research from Queue-it shows that 25% of pages could save over 250kb, and 10% could shave off more than 1MB just by compressing their assets properly.
Start with Smart Image Optimization
Images are almost always the heaviest part of a webpage, so they're the perfect place to start. The goal is to strike that delicate balance between crisp visual quality and a tiny file size. Thankfully, modern tools and formats make this easier than ever.
The first, most basic step is picking the right file format. We've all used JPEGs and PNGs for years, but it's time to embrace modern formats. WebP, for example, delivers fantastic compression and quality, often producing files 25-34% smaller than their older counterparts. It's widely supported by all major browsers now, so it’s a safe and powerful choice.
Beyond just the format, here are a few other tactics I always use:
- Compression: Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim are essential. They intelligently strip out unnecessary data from image files without any noticeable drop in quality.
- Lazy Loading: This is a game-changer. It tells the browser not to load images until a user actually scrolls them into view. Your initial page load becomes lightning fast because it’s not trying to download every single image at once.
- Responsive Images: You absolutely should not be sending a massive, high-res desktop hero image to a small mobile screen. Use the
<picture>element orsrcsetattribute to serve appropriately sized images for different devices.
Choosing the Right Image Format for Your Website
Picking the right format can feel confusing, but it’s a crucial first step. This table breaks down the most common options to help you decide what’s best for your needs.
| Format | Best For | Key Feature | Browser Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photos and complex images with many colors. | Offers a good balance of quality and file size through lossy compression. | Universal |
| PNG | Images requiring transparency (logos, icons). | Uses lossless compression, preserving every detail but at a larger size. | Universal |
| WebP | A modern replacement for both JPEG and PNG. | Provides superior lossy and lossless compression; supports transparency. | Excellent (97%+) |
| AVIF | High-quality images at very small file sizes. | The newest format with the best compression, but not yet universal. | Good (around 80%) |
| SVG | Logos, icons, and simple vector graphics. | Scalable to any size without losing quality; tiny file sizes. | Universal |
The takeaway here is simple: Use WebP as your default for most raster images. For logos and icons, SVG is almost always the right answer.
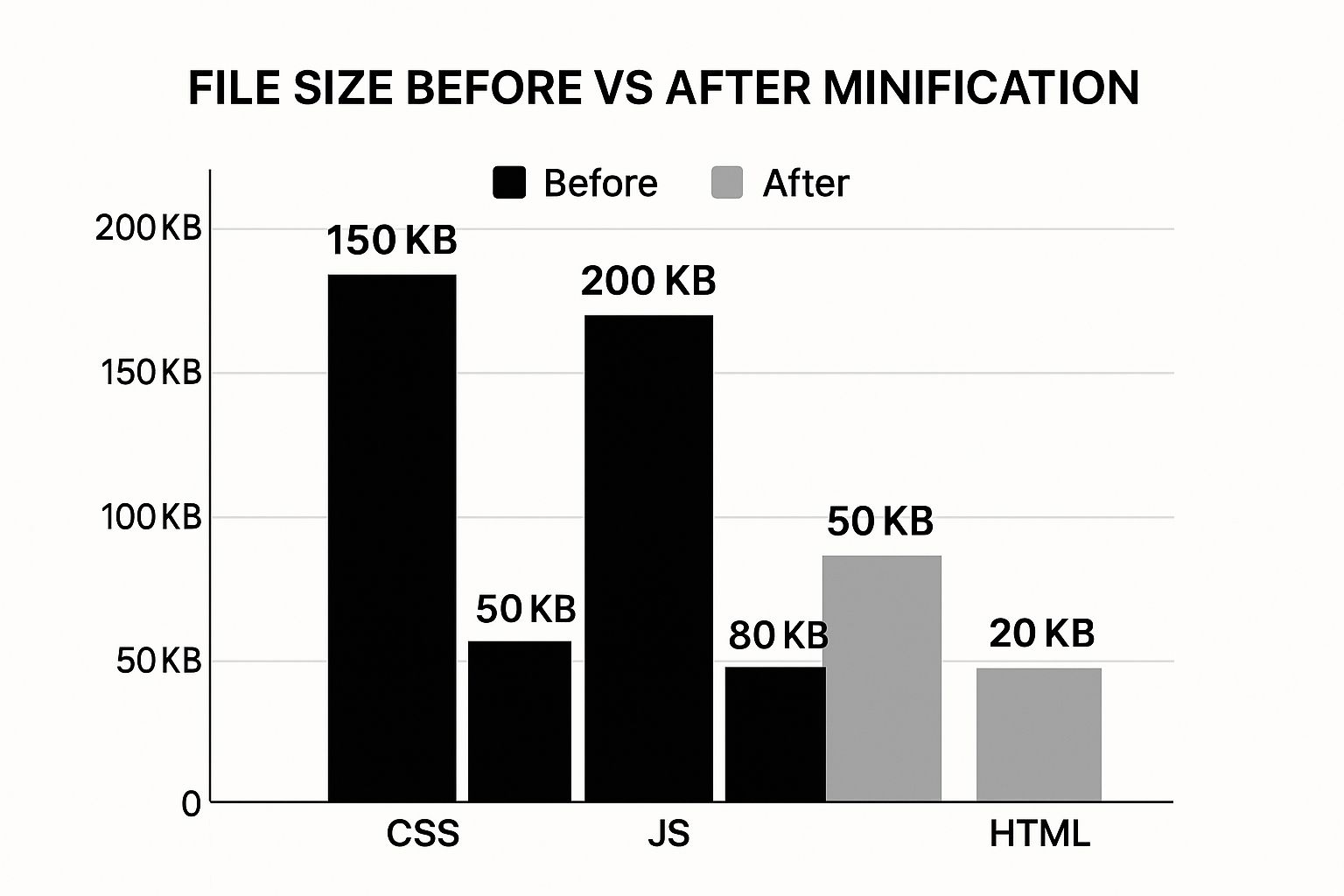
Minify and Defer Your Code
It's not just the visuals. Your CSS and JavaScript files can get chunky, too. They’re often full of comments, whitespace, and long variable names that are great for developers but completely useless to a browser.
This is where minification comes in. Minification is the process of automatically stripping all that extra stuff out of your code files. The result is a much smaller file that the browser can download and process far more quickly.
The difference can be dramatic, as you can see below.
Minifying your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML can easily cut their file sizes in half, which translates directly into a faster website.
Pro Tip: Don't stop at minification. Defer any non-critical scripts. By adding the
deferattribute to a<script>tag, you’re telling the browser, "Hey, you can go ahead and render the rest of the page; you don't have to wait for this script." This lets your most important content appear almost instantly, which massively improves how fast the site feels to a visitor.
By tackling both your images and your code, you’re hitting the two biggest sources of page bloat. This dual strategy is the key to building a lighter, faster site that your users will love.
Using Caching and CDNs for Global Performance
Okay, so you've optimized your assets—that’s a huge win. But the next frontier in the battle for speed isn't about file size; it's about distance. How far does your data have to travel to reach your user?
This is where two of the most powerful tools in our arsenal come into play: caching and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). Think of them as creating shortcuts that bring your website's content right to every visitor's doorstep, no matter where they are in the world.
When someone lands on your site for the first time, their browser has to painstakingly download every single element—images, scripts, stylesheets, the works. Caching is simply the process of telling that browser to "remember" those files. The next time they visit, the browser just pulls those assets from its local storage instead of fetching them all over again.
This simple trick makes a world of difference for returning visitors. For them, subsequent page loads can feel almost instant.
Harnessing the Power of Browser Caching
So how do you tell a browser to remember your files? You implement browser caching by setting specific instructions (HTTP headers) on your server. These headers tell browsers how long they should hold onto your site's files.
For static assets that rarely change—think your logo, fonts, or core CSS—you can set a long cache duration. I’m talking a year, even. This means a repeat visitor won't have to download those files for a very, very long time, which cuts down on HTTP requests and takes a huge load off your server. For content that changes more often, you can just set shorter expiration times.
On top of that, there's server-side caching. This works by creating static HTML versions of your dynamic pages. Instead of your server having to run a script, query a database, and build a page from scratch every single time, it serves a pre-built version. This absolutely slashes the Time to First Byte (TTFB)—the time it takes for a browser to get that very first piece of data from your server.
By combining browser and server-side caching, you create a powerful one-two punch. You're reducing the server's workload and minimizing the data that needs to be transferred. The result? A much faster experience for everyone.
Reaching a Global Audience with a CDN
A Content Delivery Network, or CDN, takes this idea of "getting closer" and applies it on a global scale. A CDN is just a network of servers distributed all over the world, and each one holds a copy of your website's static assets (images, CSS, JavaScript). These server locations are known as Points of Presence (PoPs).
Let's say your main server is in New York, but someone from Japan visits your site. Without a CDN, their request has to travel halfway around the world and back. With a CDN, their request gets routed to the nearest PoP—maybe in Tokyo. The CDN serves up your assets from there, not New York.
This simple change dramatically reduces latency, which is the delay it takes for data to travel from the server to the user.
Here’s why a CDN is a game-changer for speed:
- Reduced Latency: Content is delivered from a server physically closer to the user, shortening the travel time.
- Increased Reliability: If one server in the network goes down, traffic is automatically sent to the next closest one. No downtime.
- Lower Bandwidth Costs: The CDN handles serving your static assets, which means less traffic hitting your primary server and lower hosting bills.
If you want to get even more advanced, you can look into techniques like content prefetching, which tries to predict a user's next move. For example, Facebook has used prefetching to boost their mobile site speed by as much as 25% by preloading content from links they think a user is likely to click. You can find more on how stats like these impact user experience in this detailed analysis from Blogging Wizard.
Why Your Hosting Is Your Speed Foundation
You can spend countless hours tweaking every image and script on your site, but it's all for nothing if your web server can't keep up. Think of your hosting as the literal foundation of your website's performance. A shaky foundation means everything you build on top of it will be unstable.
It's easy to get lost in the marketing hype from hosting companies. So, let’s cut through the noise and talk about what really matters. For brand new sites, shared hosting is often the default choice. It's cheap, but there's a catch: you're sharing server resources with dozens, sometimes hundreds, of other websites. If one of those sites suddenly gets a massive traffic spike, your site can slow to a crawl.
Choosing Your Hosting Type
A big step up from shared hosting is a Virtual Private Server (VPS). You're still on a physical server with other users, but you get your own dedicated slice of its resources. This setup solves the "noisy neighbor" problem and gives you much more consistent, reliable speed. Frankly, this is my go-to recommendation for any business that's serious about its online presence.
For those who need maximum power and flexibility, cloud hosting is the answer. It’s built to be incredibly scalable, allowing your resources to expand or shrink automatically based on your traffic. Each of these hosting options directly dictates how quickly your site can even begin to respond to a visitor's request.
A key metric here is the server's Time to First Byte (TTFB). This tells you how long a browser has to wait before it receives the very first piece of data from your server. A TTFB under 200ms is fantastic, but if you see it creeping over 600ms, you've got a server-side issue that needs to be fixed.
Look Beyond the Price Tag
When I’m vetting a hosting provider, I look for a few specific, performance-focused features. A modern tech stack is absolutely essential. For example, a server running LiteSpeed instead of the older Apache can manage traffic far more efficiently and usually includes powerful, built-in caching.
Another critical detail is the physical location of the data centers. If your main audience is in the UK, you don’t want your server to be in California. Choosing a host with servers close to your users minimizes latency, which is the time it physically takes for data to travel between them and your site.
Finally, don't forget about the software running on your server. A simple update to the latest version of PHP can deliver a major performance boost, often improving how fast your site's scripts run by 20% or more. Making the right choice here isn't just a technical detail; it’s a core part of any good digital strategy because it sets the stage for every other optimization you make.
Answering Your Top Questions About Website Speed
When you first start diving into website speed optimization, it's easy to go down a rabbit hole. A few key questions always seem to come up, so let's tackle them head-on. Getting these cleared up will help you focus your energy on what truly moves the needle.
Do Tiny Speed Improvements Really Matter?
Absolutely, yes. It's easy to think a few milliseconds here or there won't make a difference, but the data tells a completely different story. That tiny fraction of a second can be the difference between a happy, returning customer and a bounce.
Think about it this way: after trimming just 0.4 seconds from its page load time, Yahoo! watched its traffic jump by 9%. On the flip side, the BBC discovered they lost 10% of their users for every extra second their site took to load.
Every tenth of a second is a competitive advantage. You can find even more compelling data in these ecommerce speed statistics on Queue-it.com.
Can't I Just Use One Big Fix, Like a CDN?
I get this question all the time. It's tempting to look for a single silver bullet—a powerful CDN or a fancy caching plugin—to solve all your speed woes. While those tools are fantastic and absolutely necessary, they can't work miracles on their own.
A CDN is great, but it's still serving whatever you give it. If you're feeding it massive, unoptimized images, it's just delivering those heavy files faster. It's not fixing the root problem. The same goes for caching; it can't compensate for a cheap, overloaded hosting server that’s slow to respond in the first place.
A holistic approach is the only one that truly works. Think of it like building a house. Your hosting is the foundation. Your code and images are the frame and walls. Caching and CDNs are the high-speed utilities. If the foundation is cracked, the rest doesn't matter much.
Should I Focus on Desktop or Mobile Speed First?
This one’s easy: prioritize mobile. No question.
For one, Google now uses mobile-first indexing. This means the mobile version of your site is what they primarily look at for ranking and indexing. If your mobile site is slow, your search visibility will suffer across the board.
Beyond that, mobile users are just more sensitive to speed. They're often on less reliable network connections and using less powerful devices. If you can create a blazing-fast experience for them under those challenging conditions, your desktop users will find your site practically instantaneous.
At Sugar Pixels, we don't just build websites; we build high-performance digital experiences. We obsess over these details so you don't have to. If you're ready for a site that's built for speed and conversions from day one, explore our web design and development services.